Table of Contents
Unlocking the mysteries of a tooth infection unveils a journey from minor discomfort to potential peril.
While a toothache may seem innocuous at first glance, the underlying infection harbors the potential to wreak havoc if left unchecked.
Delving into the depths of dental health, this comprehensive guide illuminates the trajectory of a tooth infection,
From its humble beginnings within the pulp to its potentially life-threatening consequences.
Join us as we navigate the intricate landscape of dental pathology, shedding light on the critical importance of timely intervention and proactive oral care.
Brace yourself for an insightful exploration that will equip you with the knowledge needed to safeguard your well-being against the silent dangers lurking within your smile.
Continue reading this article to gain invaluable insights into the progression of tooth infections and learn how to protect yourself from their potentially dire consequences.
Can A Tooth Infection Turn Deadly?
A tooth infection, if neglected, has the potential to evolve into a serious health concern.
When bacteria infiltrate the soft tissue within a tooth, known as the pulp, an infection ensues.
Over time, this infection may culminate in the formation of an abscess, characterized by a buildup of pus around the affected tooth.
In bygone eras, before the advent of modern dentistry, tooth infections were alarmingly common culprits of mortality.
Shockingly, historical records indicate that tooth infections accounted for 10 to 40 percent of deaths until as late as 1908.
However, advancements in dental care have significantly mitigated the mortality risk associated with tooth infections in contemporary society.
Understanding The Life-Threatening Potential

While the direct fatality risk from a tooth infection is low in modern times, the infection can precipitate severe complications if allowed to proliferate unchecked. These complications may include:
Sepsis: A systemic inflammatory response triggered by the spread of infection throughout the body.
Necrotizing Fasciitis: A severe infection causing the rapid decay of soft tissue.
Mediastinitis: Inflammation impacting the mediastinum, potentially impeding respiratory function.
Endocarditis: Inflammation of the heart’s inner lining, posing cardiac risks.
Blood Clots: Infection-induced clot formation, potentially leading to critical vascular complications.
Brain Abscess: Infection spreading to the brain, resulting in the formation of pus within cerebral structures.
Osteomyelitis: Bone tissue infection with the potential for widespread dissemination.
While not all tooth infections progress to such dire outcomes, vigilance is essential, particularly for individuals with heightened risk factors.
Identifying Risk Factors
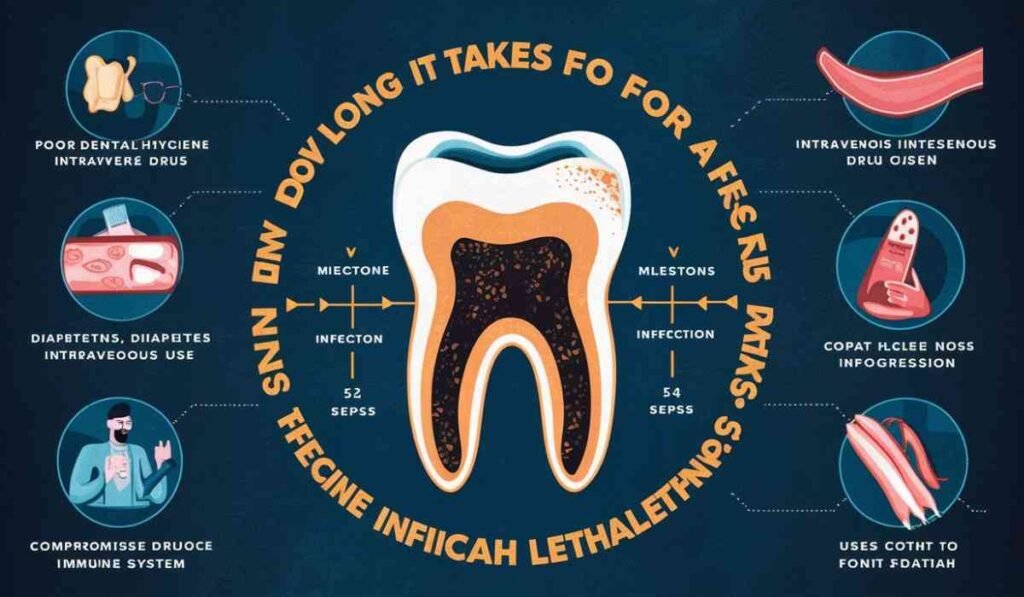
Certain factors increase susceptibility to severe complications from tooth infections:
Advanced Age: Elderly individuals face heightened vulnerability to rapid disease progression.
Diabetes: Diabetic patients are at increased risk of complications from infections, including tooth-related issues.
Immunocompromised Status: Impaired immune function amplifies susceptibility to infection-related complications.
Malnutrition: Inadequate nutrition compromises the body’s ability to combat infections effectively.
Additional Risk Factors Gleaned From External Data
Poor Dental Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing habits can exacerbate the risk of tooth infections.
High Sugar Diet: Consuming sugary foods and beverages increases the likelihood of tooth decay and subsequent infections.
Dry Mouth: Conditions leading to reduced saliva production can create an environment conducive to bacterial proliferation.
Traumatic Dental Injury: Accidents or injuries affecting the teeth can facilitate bacterial entry, hastening infection progression.
The Timeline Of Tooth Infection Progression
The evolution of a tooth infection unfolds gradually, typically beginning with the development of a tooth abscess.
Decay gradually penetrates the tooth, reaching the pulp over the course of several months.
Trauma or injury to the tooth can expedite this process, hastening bacterial infiltration into the tooth’s core.
Recognizing the signs of an abscess—manifesting as toothache and localized swelling—is pivotal.
Delayed treatment allows the infection to proliferate, potentially leading to systemic spread and life-threatening complications within days.
Preventing Catastrophic Consequences

Timely intervention is paramount in averting grave outcomes associated with tooth infections.
Antibiotics may be prescribed to arrest infection progression, alongside definitive dental treatments such as root canal therapy or tooth extraction.
Conclusion
While the immediate fatality risk from a tooth infection is low in contemporary healthcare settings, vigilance and prompt intervention are imperative.
By recognizing warning signs, adhering to preventive dental care practices, and seeking timely treatment,
Individuals can safeguard against the potentially devastating consequences of untreated tooth infections.
Stay proactive in maintaining oral health, as prevention remains the best defense against dental emergencies.
FAQs
How long does it take for a tooth infection to become life-threatening?
It can vary, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious complications within days.
What are the most common complications of untreated tooth infections?
Complications may include sepsis, abscesses, and infections in surrounding tissues or organs.
Can a tooth infection spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, if left untreated, bacteria from a tooth infection can spread to other areas, causing systemic infections.
What are the risk factors for developing severe complications from a tooth infection?
Advanced age, diabetes, immunocompromised status, and malnutrition can increase the risk of complications.
How can I prevent tooth infections and safeguard my oral health?
Practicing good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and seeking prompt treatment for dental issues can help prevent tooth infections.
What are the symptoms of a tooth infection spreading to the body?
Symptoms may include fever, fatigue, headache, swelling, difficulty breathing, and rapid heart rate.
How does a tooth become infected?
Bacteria enter the tooth through a chip, crack, or cavity, leading to decay and infection of the pulp.
When should I see a dentist for a toothache?
It’s advisable to seek dental care if a toothache persists for more than a day or is accompanied by fever, swelling, or difficulty swallowing.
What treatments are available for severe tooth infections?
Treatment options include drainage of abscesses, root canal therapy, tooth extraction, and antibiotic therapy.
What can I do at home to alleviate symptoms of a tooth infection?
Home remedies may include over-the-counter pain medications, soft diet, saltwater rinses, cold compresses, and garlic application, but these should not replace professional dental care.